| [1] Lobo V,Patil A,Phatak A,et al.Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health.Pharmacogn Rev.2010;4(8):118-126.[2] Uhl L,Gerstel A,Chabalier M,et al.Hydrogen peroxide induced cell death: one or two modes of action.Heliyon.2015;1(4):e00049.[3] Rahman K.Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors.Clin Interv Aging.2007; 2(2): 219-236.[4] Morita M,Naito Y,Yoshikawa T,et al.Plasma lipid oxidation induced by peroxynitrite, hypochlorite, lipoxygenase and peroxyl radicals and its inhibition by antioxidants as assessed by diphenyl-1-pyrenylphosphine. Redox Biol.2016;8:127-135.[5] Aslani BA,Ghobadi S.Studies on oxidants and antioxidants with a brief glance at their relevance to the immune system.Life Sci. 2016;146: 163-173.[6] Ranchoux B,Meloche J,Paulin R,et al.DNA damage and pulmonary hypertension.Int J Mol Sci.2016;17(6):990.[7] Niedzielska E,Smaga I,Gawlik M,et al.Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mol Neurobiol.2016;53(6):4094-4125.[8] Hofer T,Perry G.Nucleic acid oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease-explained by the hepcidin-ferroportin neuronal iron overload hypothesis?J Trace Elem Med Biol.2016;38:1-9.[9] Bonomini F,Rodella LF,Rezzani R.Metabolic syndrome, aging and involvement of oxidative stress.Aging Dis.2015;6(2):109-120.[10] Salvayre R,Negre-Salvayre A,Camaré C.Oxidative theory of atherosclerosis and antioxidants.Biochimie. 2016;125:281-296.[11] Prasad S,Gupta SC,Pandey MK,et al.Oxidative stress and cancer: advances and challenges. Oxid Med Cell Longev.2016;2016:1.[12] Wang JH,Li B.Mechanics rules cell biology.Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol.2010; 2(16):1-7.[13] Del SL,Slutsky AS.Acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure.Curr Opin Crit Care.2011;17(1):1-6.[14] Tian YFg,Gawlak G,O'Donnell JJ,et al.Modulation of Endothelial Inflammation by Low and High Magnitude Cyclic Stretch.PloS One. 2016;11(4):1-13.[15] Xia J,Li R,Yang R,et al.Mild hypothermia attenuate kidney injury in canines with oleic acid-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Injury.2016;47(7):1445-1451.[16] Chapman KE,Sinclair SE,Zhuang D,et al.Cyclic mechanical strain increases reactive oxygen species production in pulmonary epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2005;289: L834-L841.[17] Davidovich N,DiPaolo BC,Lawrence GG,et al.Cyclic Stretch-Induced Oxidative Stress Increases Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Permeability. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.2013;49(1):156-164.[18] Kuhn H,Nieuwenhuijsen H,Karthe B,et al.Stretch-induced apoptosis in rat alveolar epithelial cells is mediated by the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway.Exp Lung Res.2017;43(1):49-56.[19] Wu J,Yan Z,Schwartz DE,et al.Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in alveolar macrophages contributes to mechanical stretch-induced lung inflammation and injury.J Immunol.2013;190(7): 3590-3599.[20] Chiang CH,Chuang CH,Liu SL,et al.N-acetylcysteine attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in an isolated and perfused rat lung model.Injury.2012;43:1257-1263.[21] Dong WW,Liu YJ,Lv Z,et al.Lung endothelial barrier protection by resveratrol involves inhibition of HMGB1 release and HMGB1-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage via an Nrf2-dependent mechanism.Free Radic Biol Med.2015;88(Pt B):404-416. [22] Makena PS,Gorantla VK,Ghosh MC,et al.Lung injury caused by high tidal volume mechanical ventilation and hyperoxia is dependent on oxidant-mediated c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation.J Appl Physiol. 2011;111:1467-1476.[23] Hsieh HJ,Liu CA,Huang B,et al.Shear-induced endothelial mechanotransduction: the interplay between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) and the pathophysiological implications.J Biomed Sci.2014;21(3):1-15.[24] Matlung HL,Bakker EN,Van Bavel E.Shear stress, reactive oxygen species, and arterial structure and function.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11(7):1699-1709.[25] Birukov KG.Cyclic Stretch, reactive oxygen species, and vascular remodeling.Antioxid Redox Signal.2009;11(7):1651-1667.[26] Montezano AC,Cat AND,Rios FJ,et al.Angiotensin II and vascular injury.Curr Hypertens Rep.2014;16(6):431. [27] Bentzon JF,Otsuka F,Virmani R,et al.Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture.Circ Res. 2014;114(12):1852-1866.[28] Millon A,Sigovan M,Boussel L,et al.Low WSS Induces Intimal Thickening, while Large WSS Variation and Inflammation Induce Medial Thinning, in an Animal Model of Atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0141880.[29] Gopal DM,Santhanakrishnan R,Wang YC,et al.Impaired right ventricular hemodynamics indicate preclinical pulmonary hypertension in patients with metabolic syndrome.J Am Heart Assoc.2015; 4:e001597.[30] Liu X,Peyton KJ,Durante W.Physiological cyclic strain promotes endothelial cell survival via the induction of heme oxygenase-1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2013;304(12):H1634-H1643.[31] Liu JC,Chen JJ,Chan P,et al.Inhibition of cyclic strain-induced endothelin-1 gene expression by resveratrol.Hypertension. 2003;42: 1198-1205.[32] Matsushita H,Lee K,Tsao PS.Cyclic strain induces reactive oxygen species production via an endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase.J Cell Biochem Suppl.2001;36:99-106.[33] Shinmura A,Tsukamoto A,Hamada T,et al.Morphological dynamics of mitochondria in bovine aortic endothelial cell under cyclic stretch.Adv Biomed Eng.2015;4:60-66.[34] Chin LK,Yu JQ,Fu Y,et al.Production of reactive oxygen species in endothelial cells under different pulsatile shear stresses and glucose concentrations.Lab Chip.2011;11(11):1856-1863.[35] Ding Z,Liu S,Wang Xi,et al.Hemodynamic shear stress via ROS modulates PCSK9 expression in human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells and along the mouse aorta.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;22(9):760-771.[36] Mata-Greenwood E,Meyrick B,Soifer SJ,et al.Expression of VEGF and its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1/KDR is altered in lambs with increased pulmonary blood flow and pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2003;285(1):L222-L231.[37] Mata-Greenwood E,Grobe A,Kumar S,et al.Cyclic stretch increases VEGF expression in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells via TGF-β1 and reactive oxygen species: a requirement for NAD(P)H oxidase.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2005;289(2):L288-L298.[38] Wedgwood S,Lakshminrusimha S,Schumacker PT,et al.Cyclic stretch stimulates mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and Nox4 signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2015;309:L196-L203.[39] Dick AS,Ivanovska J,Kantores C,et al.Cyclic stretch stimulates nitric oxide synthase-1-dependent peroxynitrite formation by neonatal rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Free Radic Biol Med.2013;61: 310-319.[40] Chen Q,Li W,Quan Z,et al.Modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell alignment by cyclic strain is dependent on reactive oxygen species and P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.J Vasc Surg. 2003;37(3): 660-668.[41] Grote K,Flach I,Luchtefeld M,et al.Mechanical stretch enhances mRNA expression and proenzyme release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) via NAD(P)H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species.Circ Res.2003;92:e80-e86.[42] Ellulu MS,Patimah I,Khaza'ai H,et al.Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a review of initiators and protective factors. Inflammopharmacology.2016;24(1):1-10.[43] Greene MA,Loeser RF.Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1966-1971.[44] Yui N,Yudoh K,Fujiya H,et al.Mechanical and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis.J Phys Fit Sports Med.2016;5(1):81-86.[45] Ward CW,Prosser BL,Lederer WJ.Mechanical stretch-induced activation of ROS/RNS signaling in striated muscle.Antioxid Redox Signal.2014;20(6):929-936. [46] Liu X,Zhou D,Xie T,et al.Nrf2, a potential therapeutic target against oxidative stress in corneal diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017; 2017:1-9.[47] Arnal E,Peris-Martínez C,Menezo JL,et al.Oxidative Stress in Keratoconus?Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2011;52(12):8592-8597.[48] Kiliç R,Cumurcu T,Sancaktar E,et al.Systemic Prolidase Activity and Oxidative Stress in Keratoconus.Curr Eye Res.2016;41(1):28-33.[49] Cantemir A,Alexa AI,Ciobica A,et al.Evaluation of atioxidant enzymes in keratoconus. Revista de Chimie.2016;67(8):1538-1541.[50] Kovac S,Angelova PR,Holmström KM,et al.Nrf2 regulates ROS production by mitochondria and NADPH oxidase.Biochim Biophys Acta.2015;1850(4):794-801.[51] Rodiño-Janeiro BK,Paradela-Dobarro B,Raposeiras-Roubín S,et al.Glycated human serum albumin induces NF-κB activation and endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.J Diabetes Complications.2015;29(8): 984-992.[52] Xiong S,Wang P, Ma L,et al.Ameliorating Endothelial Mitochondrial Dysfunction Restores Coronary Function via Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1-Mediated Protein Kinase A/Uncoupling Protein 2 Pathway.Hypertension.2016;67(2):451-460.[53] Battelli MG,Polito L,Bortolotti M,et al.Xanthine Oxidoreductase-Derived Reactive Species: Physiological and Pathological Effects.Oxid Med Cell Longev.2016;2016:3527579.[54] Schramm A,Matusik P,Osmenda G,et al.Targeting NADPH oxidases in vascular pharmacology. Vasc Pharmacol.2012;56(5-6):216-231.[55] Marin T,Gongol B,Chen Z,et al.Mechanosensitive microRNAs-Role in endothelial responses to shear stress and redox state.Free Radic Biol Med.2013;64(6):61-68.[56] Amanso AM,Griendling KK.Differential roles of NADPH oxidases in vascular physiology and pathophysiology.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012;4(1):1044-1064.[57] Frey RS,Gao X,Javaid K,et al.Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma signaling through protein kinase Czeta induces NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidant generation and NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells.J Biol Chem.2006;281(23):16128-16138.[58] Tkachev VO,Menshchikova EB,Zenkov NK.Mechanism of the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling system.Biochemistry. 2011;76(4):407-422.[59] Cho HY,Kleeberger SR.Association of Nrf2 with airway pathogenesis: lessons learned from genetic mouse models.Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(11): 1931-1957. [60] Klaassen CD,Reisman SA.Nrf2 the rescue: effects of the antioxidative/electrophilic response on the liver.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;244(1):57-65.[61] Ashino T,Yamamoto M,Numazawa S.Nrf2/Keap1 system regulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis for vascular homeostasis: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury.Sci Rep. 2016;6(26291): 1-12. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:是指机体在受到各种内源性或外源性刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧、活性氮等产生过多,使氧化和抗氧化系统失衡,破坏许多生物大分子的正常功能,从而导致细胞或组织氧化损伤,引发多种疾病的发生发展。
细胞力学生物学:力学生物学是探讨力学环境(刺激)对生物体健康、疾病或损伤的影响,研究生物体的力学信号感受和响应机制,阐明机体的力学过程与生物学过程如生长、重建、适应性变化和修复等之间的相互关系。
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指机体在受到各种内源性或外源性刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧、活性氮等产生过多,使氧化和抗氧化系统失衡,破坏许多生物大分子的正常功能,从而导致细胞或组织氧化损伤,引发多种疾病的发生发展。
细胞力学生物学:力学生物学是探讨力学环境(刺激)对生物体健康、疾病或损伤的影响,研究生物体的力学信号感受和响应机制,阐明机体的力学过程与生物学过程如生长、重建、适应性变化和修复等之间的相互关系。.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:是指机体在受到各种内源性或外源性刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧、活性氮等产生过多,使氧化和抗氧化系统失衡,破坏许多生物大分子的正常功能,从而导致细胞或组织氧化损伤,引发多种疾病的发生发展。
细胞力学生物学:力学生物学是探讨力学环境(刺激)对生物体健康、疾病或损伤的影响,研究生物体的力学信号感受和响应机制,阐明机体的力学过程与生物学过程如生长、重建、适应性变化和修复等之间的相互关系。
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指机体在受到各种内源性或外源性刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧、活性氮等产生过多,使氧化和抗氧化系统失衡,破坏许多生物大分子的正常功能,从而导致细胞或组织氧化损伤,引发多种疾病的发生发展。
细胞力学生物学:力学生物学是探讨力学环境(刺激)对生物体健康、疾病或损伤的影响,研究生物体的力学信号感受和响应机制,阐明机体的力学过程与生物学过程如生长、重建、适应性变化和修复等之间的相互关系。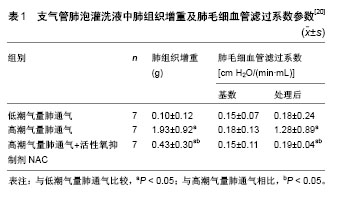
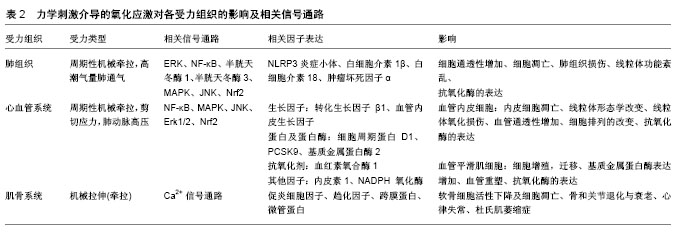
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
氧化应激:是指机体在受到各种内源性或外源性刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧、活性氮等产生过多,使氧化和抗氧化系统失衡,破坏许多生物大分子的正常功能,从而导致细胞或组织氧化损伤,引发多种疾病的发生发展。
细胞力学生物学:力学生物学是探讨力学环境(刺激)对生物体健康、疾病或损伤的影响,研究生物体的力学信号感受和响应机制,阐明机体的力学过程与生物学过程如生长、重建、适应性变化和修复等之间的相互关系。
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指机体在受到各种内源性或外源性刺激时,体内高活性分子如活性氧、活性氮等产生过多,使氧化和抗氧化系统失衡,破坏许多生物大分子的正常功能,从而导致细胞或组织氧化损伤,引发多种疾病的发生发展。
细胞力学生物学:力学生物学是探讨力学环境(刺激)对生物体健康、疾病或损伤的影响,研究生物体的力学信号感受和响应机制,阐明机体的力学过程与生物学过程如生长、重建、适应性变化和修复等之间的相互关系。